- Unprivileged user subjects, which are used for routine data access by ordinary users of the system. For convenience, this specification refers to such subjects as user certificate.
- Data Recovery Agents (DRAs), which are controlled by system administrators. The storage system ensures that all active DRAs for the system are automatically authorized to access all encrypted objects on the system. If an unprivileged user loses the private key, an administrator can use a DRA's private key to recover the contents of encrypted objects.
EFSRPC also assumes that each encrypted object is associated with some security-related metadata, which contains information required for authorized users and DRAs to access the plaintext of the object. This specification refers to this security-related metadata as the EFSRPC Metadata.
EFSRPC does not specify how data is encrypted, stored, or accessed. It is possible to build a compliant EFSRPC implementation that uses a mechanism, such as access control lists (ACLs), instead of encryption to control access to data objects. For the purposes of this specification, the term encrypted is used to indicate that a data object and its metadata can be successfully manipulated through the EFSRPC methods, with the exception of the EfsRpcEncryptFileSrv method, which converts data objects from an unencrypted state to an encrypted state.
Within the preceding model, EFSRPC provides various categories of management routines. The syntax of the individual methods and rules for how these methods are processed on the server are specified in section 3.1.4.2. The categories of management routines that EFSRPC provides are as follows:
- Requesting the server to convert objects from encrypted state to unencrypted state and vice versa.
- EfsRpcEncryptFileSrv (section 3.1.4.2.5)
- EfsRpcDecryptFileSrv (section 3.1.4.2.6)
- EfsRpcQueryUsersOnFile (section 3.1.4.2.7)
- EfsRpcQueryRecoveryAgents (section 3.1.4.2.8)
- EfsRpcRemoveUsersFromFile (section 3.1.4.2.9)
- EfsRpcAddUsersToFile (section 3.1.4.2.10)
- EfsRpcFileKeyInfo (section 3.1.4.2.12)
- EfsRpcDuplicateEncryptionInfoFile (section 3.1.4.2.13)
- EfsRpcAddUsersToFileEx (section 3.1.4.2.14)
- EfsRpcFileKeyInfoEx (section 3.1.4.2.15)
- EfsRpcGetEncryptedFileMetadata (section 3.1.4.2.16)
- EfsRpcSetEncryptedFileMetadata (section 3.1.4.2.17)
- EfsRpcOpenFileRaw (section 3.1.4.2.1)
- EfsRpcReadFileRaw (section 3.1.4.2.2)
- EfsRpcWriteFileRaw (section 3.1.4.2.3)
- EfsRpcCloseRaw (section 3.1.4.2.4)
- EfsRpcFlushEfsCache (section 3.1.4.2.18)
Most of the EFSRPC routines are stateless and can be called in any order. When one of these routines is called, the message exchange is as follows.
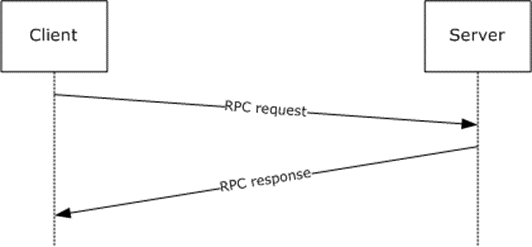
Figure 1: Message exchange for stateless routines
There are two routines in EFSRPC that are an exception to the stateless nature of the protocol. Several methods, collectively known as the EFSRPC raw methods, are an exception and need to be called in a specific order. This includes the EfsRpcOpenFileRaw, EfsRpcReadFileRaw, EfsRpcWriteFileRaw, and EfsRpcCloseRaw methods. The following two sequences are permissible.
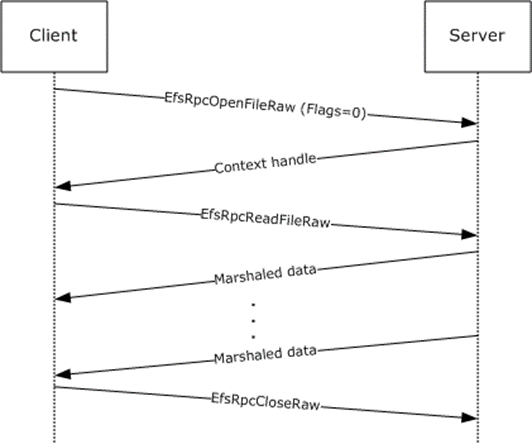
Figure 2: Message sequence for opening a file
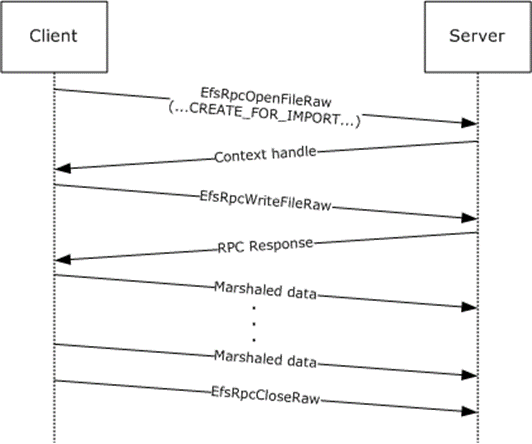
Figure 3: Message sequence for importing a file